-
Database Security and Strategy
-
Database Security Assessment
-
Deliverable Report Information
-
Database Security Strategy
-
Key Pillars of Database Security Strategy
Database Security and Strategy
With a growing number of internal and external attacks on corporate and public applications and robust regulatory compliance enforcements, data security continues to be the highest priority for enterprises and governments year after year. Even though many enterprises are taking stronger measures to protect their data, substantial gaps still persist at the very core i.e. the databases which contain the corporate crown jewels.
Many enterprises don’t have a database security strategy that can defend against sophisticated attacks originating externally or internally, track sensitive information as it’s copied to numerous locations, or even meet the harder evolving regulatory requirements. In addition, most of the businesses tend to emphasize more on the detective controls rather than the preventive measures and controls when it comes to database security, making them highly vulnerable. By contrast, it is observed that companies that implemented a comprehensive and integrated database security product with a solid emphasis on preventive controls attained better security controls introduced a higher degree of automation through the organization, and were more confident in defending against attacks.
Database Security Assessment
The key focus is to review and assess the database environment to understand configuration weaknesses that may impact the security of the database environment.
Using our customized scripts and tools key security information is extracted for:
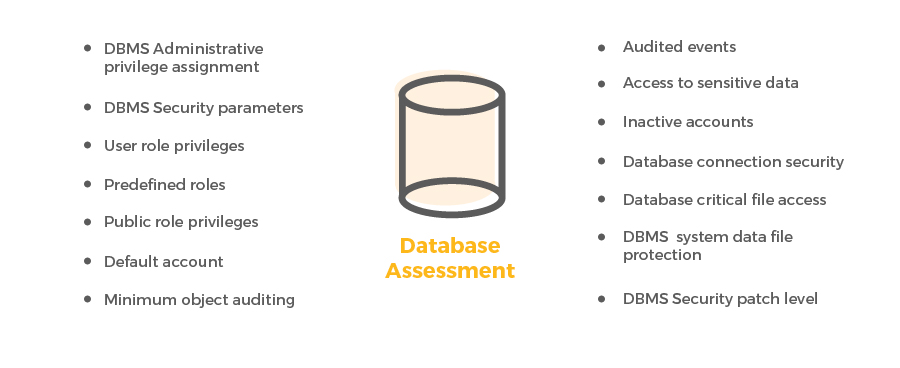
From a security review perspective – we also emphasize on the following as a part of our overall approach:
- Circulate questionnaires and conduct discussions with process owners and data owners to understand how the data flows through each of the prioritized process areas identified in Phase 1
- Inventory applications and databases based on the identified business processes in Phase 1
- Understand the sensitive data elements (e.g., credit card number, customer name, date of birth, medication information, diagnostics, etc.) via interviews and questionnaires
- Review existing security controls in place for the protection of sensitive data and analyze if these controls are appropriate
- Align identified sensitive data to organization’s current data classification levels
Deliverable Report Information
Document risks, gaps, areas of improvement and observations including a high-level strategy to address test data requirements:
- Understand HR practices (communication to data owners when an employee or contactor resigns, or when an employee’s job role is changed, etc.)
- Assess proliferation of the data from secure to non-secure locations
- Conduct discussions and understand existing process policies and procedures for access management (e.g., access request, granting and maintenance including disabling of access)
- Using databases identified during the database assessment conduct limited access review of users to understand if access privileges assigned are aligned to business requirements;
Database Security Strategy
A database security strategy focuses on proactively protecting data from internal and external attacks, curtailing data exposure to privileged and authorized IT users, and safeguarding all databases, including production and non-production.
Furthermost organizations generally focus on perimeter centered network security, proposing the first line of defense, but increasing complexity of an organization’s security environment and sophisticated attack vectors require organizations to take a comprehensive view of data security. Database security, which is the generally considered the last line of defense for enterprise data, needs a much larger focus than other layers of the whole stack for the reason that it holds an organization’s crown jewels.
A key to build any successful database security strategy encompasses:
- Understanding what type of data including the data which needs to be protected, such as personal identification information (PII), credit card numbers, customer data, Social Security Numbers protected, Intellectual property and health information etc.
- Understanding applicable regulatory compliance requirements, such as Payment Card Industry (PCI), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), FISMA etc.
- Performing an inventory of all databases, including nonproduction.
- Discovering and classifying databases based on the sensitivity of data.
- Establishing security policies for all databases in the environment segregated across zones.
- Having actions for each category of policies and deploying them across databases segregated across zones.
- Taking suitable security measures, such as data masking (redaction), monitoring, auditing, encryption and access control.
- Looking for a all – inclusive database security solution that can implement a robust database security at a low cost.
Key Pillars of Database Security Strategy
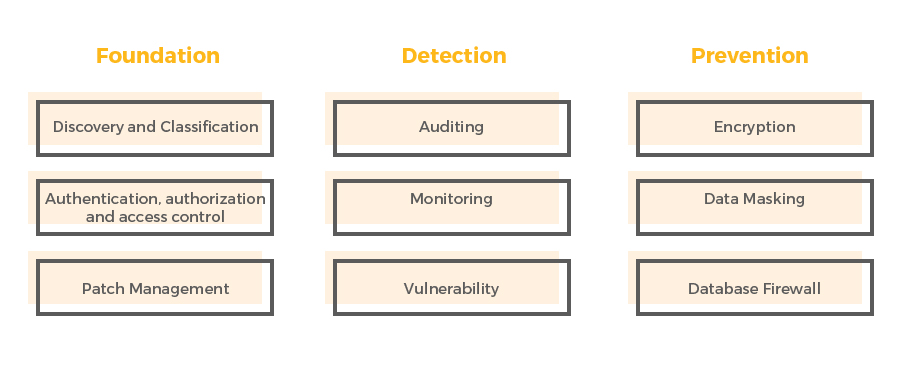
Foundation Pillar
This primarily includes Discovery, Classification, AAA – Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting, and Patch Management. Without understanding where and how the sensitive data is used across the environment, securing data can get very sophisticated and challenging. The ‘foundation pillar’ stresses on discovery and classification of sensitive data and devising a vigorous authentication, authorization, and access control framework. In addition, all critical databases must be patched periodically basis to remove known vulnerabilities.
Understanding which all databases encompasses sensitive data is an important requirement for any database security strategy and architecture. Organizations should take a comprehensive inventory of all databases, including all environments across enterprise (such as production and non-production), and confirm authentication, authorization, and access control is enabled for all business sensitive and critical databases.
For establishing a strong database security foundation, enterprises should use:
- Database discovery and classification – which provides information on which all databases to focus upon
- AAA mechanisms (Authentication, authorization, and access control) for appropriate database access
- Patch management protecting against identified vulnerabilities
Detection Pillar
This section encompasses Monitoring, Auditing, and Vulnerability Assessment. All changes to sensitive data should be logged to provide the ability to justify and respond to auditing wherein the importance is on “who changed what data?”, “when was it changed?” etc. Auditing and monitoring also usually compromises of compensating controls when preventive measures are not enabled. In addition, vulnerability assessment reports gaps in the database environment, such as weak passwords or excessive access privileges.
To support regulatory compliance standards, such as PCI, HIPAA, FISMA, etc. and improve data security, organizations should have records of all accesses and modifications to sensitive data. Data and metadata within databases can be accessed, modified, or even deleted in moments. Detection pillar emphasizes on comprehensive audit trail of database activities and make available details on vulnerabilities.
Detection layer security fundamentally includes:
- Continuous auditing and alerting on data anomalies and access by privileged users
- Security monitoring and real-time intrusion prevention to defend the database against potential threats
- Vulnerability assessment to check for database integrity and security configuration across databases
Preventive Pillar
This category encompasses Data Encryption, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. These pillar emphases on preventing unauthorized access and protecting against potential attacks.
Preventive security measures essentially consists of:
- Network and data-at-rest encryption.
- Data masking (redaction) across all databases to prevent data exposure to all the category of users including but not restricted to developers, testers, and other non-production users.
- Database firewall to prevent potential threats such as SQL injection attacks or privilege escalation from impacting databases.
- Change management to enable a formal procedure to manage changes in production. The goal is to prevent unauthorized access to and exposure of private data.
Preventive measures basically include:
- Data redaction / masking to protect data in nonproduction databases.
- Database and network encryption to defend databases and applications across all the network zones.
- Database firewall ensures real-time protection from multiple attack vectors and ensures that if any unauthorized users gets access, it can protect the corresponding data by blocking connection or relevant access in real time.
Our Thoughts
Database security has become critical for all enterprises to defend against growing attacks and meeting various regulatory requirements.
Based on our experience below are the key takeaways from such form of assessments:
- Prevention should be a topmost priority as per the architecture – Even though database monitoring is vital to track data access, it doesn’t prevent cyber criminals and hackers from stealing data. Organizations must commence looking at making the most of their focus by implementing preventive controls via hardening configuration etc. to protect against real-time sophisticated threats.
- Focus on an organization wide database security strategy – An all-inclusive database security strategy makes sure that investments are not ad hoc and address the three key pillars — foundation, detection, and prevention across the critical databases. Don’t just focus on one or two critical databases, but on all databases that store sensitive data in other words, all your databases.

